
|
| Home < Products < Acoustic Measurement < HeadZap | ||||
|
HeadZap™
Measure Acoustic Head Maps (HRTFs) in the Real World |
||||
 Simulation of 3D audio employs filters containing characteristics of
the head, torso, and pinna. The accuracy of these Head-Related
Transfer Functions (HRTF) filters directly affects the quality of the
synthesized sound. Research shows that using listener-specific HRTFs
significantly improves localization precision. Simulation of 3D audio employs filters containing characteristics of
the head, torso, and pinna. The accuracy of these Head-Related
Transfer Functions (HRTF) filters directly affects the quality of the
synthesized sound. Research shows that using listener-specific HRTFs
significantly improves localization precision.Until recently, measuring individualized HRTFs was a costly and lengthy process that could only be performed in highly controlled acoustic environments, often requiring expensive custom software and hardware components. HeadZaptm is a commercially available acoustic measurement system designed to measure HRTFs in a less controlled (and less costly) environment. It is an essential tool for hearing research, virtual auditory environment modeling, and 3D sound simulation. Capturing a complete map of acoustic measurements for a specific individual is fast and easy and can be performed in untreated rooms. |
||||
 Traditional Methods
Traditional MethodsHead-related transfer functions are traditionally measured directly by analyzing sound waves arriving at a listenerís ear canal that have originated from known audio sources placed at various locations about the listener. Typically, the subject position is fixed, and a vertical, semi-circular arc array of speakers, mechanically swept to azimuth increments around the subject, is used to generate the needed HRTF directions. Swept sinusoids or maximum-length sequences are often used as test signals, and probe microphones make measurements near the eardrums. So that unwanted reflections do not corrupt the data, the subject and speaker array are placed in an anechoic chamber. HeadZap Approach Like most systems currently in use, HeadZap provides a direct acoustic HRTF measurement. HeadZap, however, was designed for use in the reflective, noisy settings typical of offices and laboratories.  Instead of using
an array of loudspeakers, HeadZap uses a single speaker mounted on a
vertically-sliding arm. The loudspeakerís position is fixed for
every ring, changing only every time measurements for a new elevation
are needed. The subject is seated on a rotating stool and adjusts
his/her position according to the desired HRTF location. The benefits
of using a single versus an array of speakers are twofold. Instead of using
an array of loudspeakers, HeadZap uses a single speaker mounted on a
vertically-sliding arm. The loudspeakerís position is fixed for
every ring, changing only every time measurements for a new elevation
are needed. The subject is seated on a rotating stool and adjusts
his/her position according to the desired HRTF location. The benefits
of using a single versus an array of speakers are twofold.First, the need to calibrate the multiple speakers and perform free-field equalization is eliminated as the speaker-microphone characteristics are preserved between measurements. Second, the system is very portable and easy to assemble. 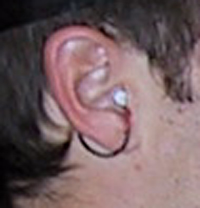 To increase measurement signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) so as to overcome
the effects of noise, the subject is outfitted with blocked meatus
microphones which gather considerably more signal than do probe microphones,
and permit louder test sequences to be used. Probe microphones are
often custom-fitted and painfully intrusive to the subject.
Blocked-meatus microphones are no more intrusive than earplugs.
To increase measurement signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) so as to overcome
the effects of noise, the subject is outfitted with blocked meatus
microphones which gather considerably more signal than do probe microphones,
and permit louder test sequences to be used. Probe microphones are
often custom-fitted and painfully intrusive to the subject.
Blocked-meatus microphones are no more intrusive than earplugs.Rather than eliminating reflections from the measurement environment, the approach taken by HeadZap is to extract only the direct path contribution from the measurements. Extraction of raw HRTF data is performed by windowing the measurements such that no room reflections are incorporated in the compilation of the final data. AuSIM PART NUMBERS ... AuHZ100 -HeadZap Upgrade to a GoldSeries server SYSTEM COMPONENTS SYSTEM SPECIFICATIONS BROCHURE ... DOWNLOAD |
||||
|
|
||

|
[Home] [About AuSIM] [Products] [Services] [Applications] |
|
| [Support] [Contacts] [Buy Online] [Downloads] [News & Events] | ||
| © AuSIM Inc. 1998-2011. Last updated on | ||